Introduction
Soil samples contain a large number of microorganisms, the vast majority of which can not be directly cultivated for reproduction and research. Extracting DNA from soil samples is the most effective method for studying soil microorganisms. At present, there are mainly direct and indirect methods for extracting microbial DNA from soil samples. The direct method refers to placing soil samples in the lysis solution, and using effective wall breaking methods to release all microbial DNA into the lysis solution, followed by separation and extraction, such as Zhou's method. Indirect method refers to placing soil in a buffer, such as Buffer PBS, to separate microorganisms from the soil and then extract DNA. The indirect method can greatly reduce the impact of humic acids and heavy metal salts on DNA extraction in soil, but this method will lose many microorganisms and the resulting DNA is not the entire genome (metagenome) of the soil sample. Currently, few researchers have adopted this method. Extracting DNA directly from soil samples can maximize the likelihood of obtaining the entire genome, but this method faces the following issues:
1. Humic acid pollution. The soil, especially in forests and grasslands, is rich in humic acids. Humic acid is a series of organic molecules, some of which are very similar to nucleic acid molecules and difficult to remove during purification. Trace amounts of humic acid pollution can lead to downstream applications such as PCR and enzyme digestion failure.
2. Lysis method. Soil samples contain various microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. Gram positive bacteria and fungi both contain very thick bacterial walls, and effectively breaking down the cell walls of these microorganisms is crucial for extracting high-yield metagenomic DNA. Due to the complexity of soil samples, it is not feasible to use enzymatic methods (such as lysozyme, wall breaking enzyme, snail enzyme) or liquid nitrogen grinding, as the soil contains various metalions or inhibitory factors that inactive the digestive enzymes, or the presence of sand particles in the soil makes liquid nitrogen grinding difficult.
3. The DNA yield is difficult to control. Soil samples would have significant changes in the number and variety of microorganisms due to fertility, inferiority, high moisture content, dryness, or depth of sampling. In a small range of soil samples, the DNA content often varies by thousands of times. In addition, certain chemical components in soil, such as heavy metal salts and clay substances, can cause a decrease in DNA yield.
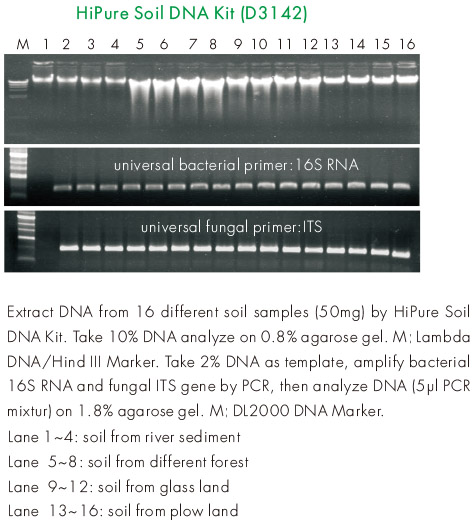
Magen's HiPure Soil DNA Kits are currently the most optimized kit for soil DNA extraction. The kit adopts glass bead grinding method and thermal shock chemical wall breaking method, which can be carried out in the point vortex instrument without special bead grinding instrument, and is suitable for a wide range of laboratories. The Absorber Solution in the reagent kit is a humic acid adsorbent exclusively developed by Magen Company, which can efficiently remove various humic acid pollutants. In addition, an alcohol-free silica gel column purification method is also used to efficiently remove various soluble metal salts and other soluble inhibitory factors from the soil. The kit has successfully extracted from the following soil (partially based on customer feedback): soil from forests in nature reserves (30 to 40 years old forest soil with a surface layer of 30-50cm deciduous layer), mangrove soil, grasslands, farmland, seabed mud, sludge, mineral area soil, organic matter contaminated soil, pond mud, garbage mud, air conditioning pipeline deposits, etc.